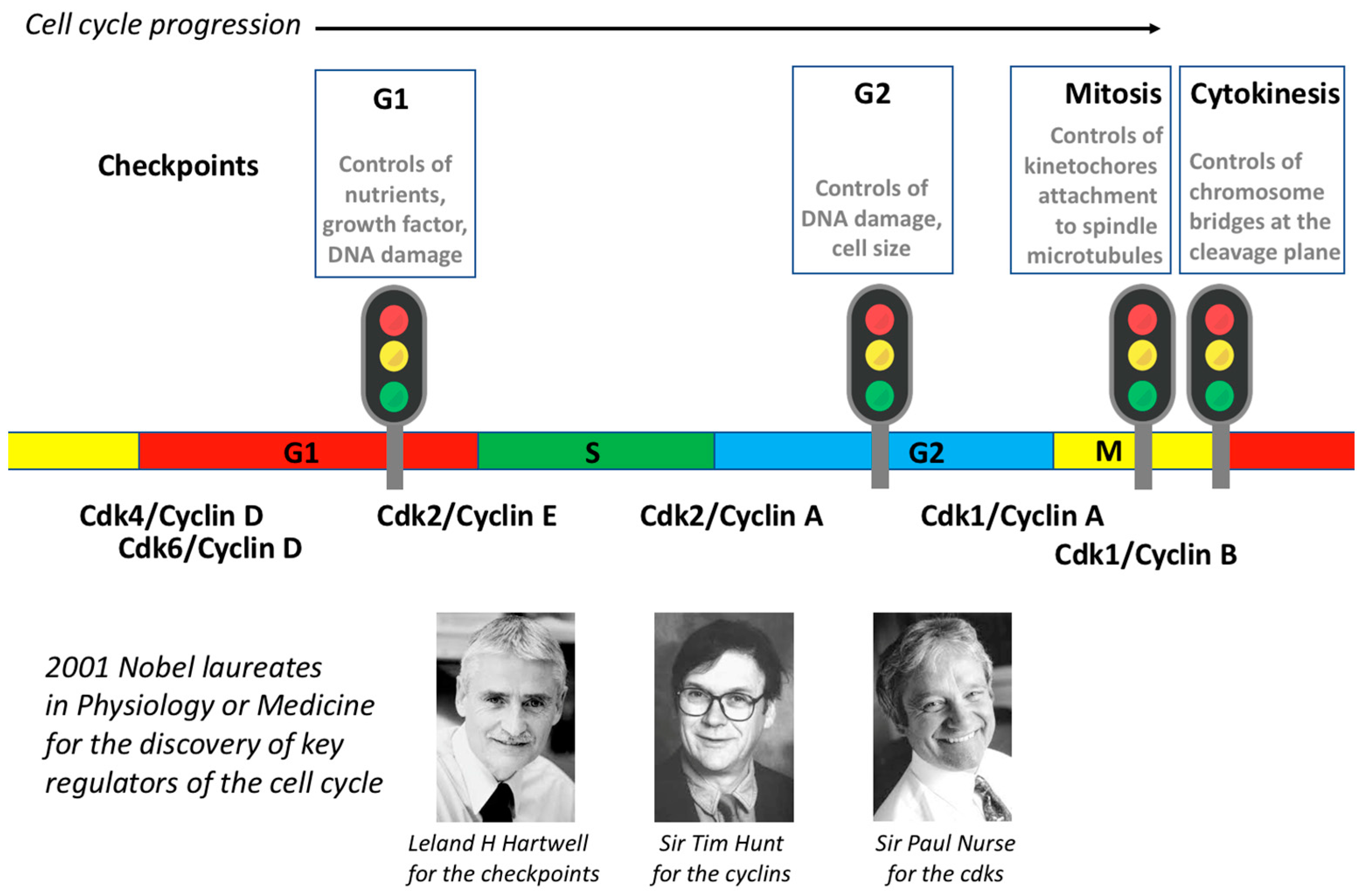
CELL CYCLE Biology Diagrams The cell cycle is a cycle of stages that cells pass through to allow them to divide and produce new cells. It is sometimes referred to as the "cell division cycle" for that reason. When the S phase is completed, the cell will have two complete sets of its genetic material. This is crucial for cell division, as it ensures that both

The Cell-Cycle Control System Can Be Analyzed Biochemically in Animal Embryos. While yeasts are ideal for studying the genetics of the cell cycle, the biochemistry of the cycle is most easily analyzed in the giant fertilized eggs of many animals, which carry large stockpiles of the proteins needed for cell division.
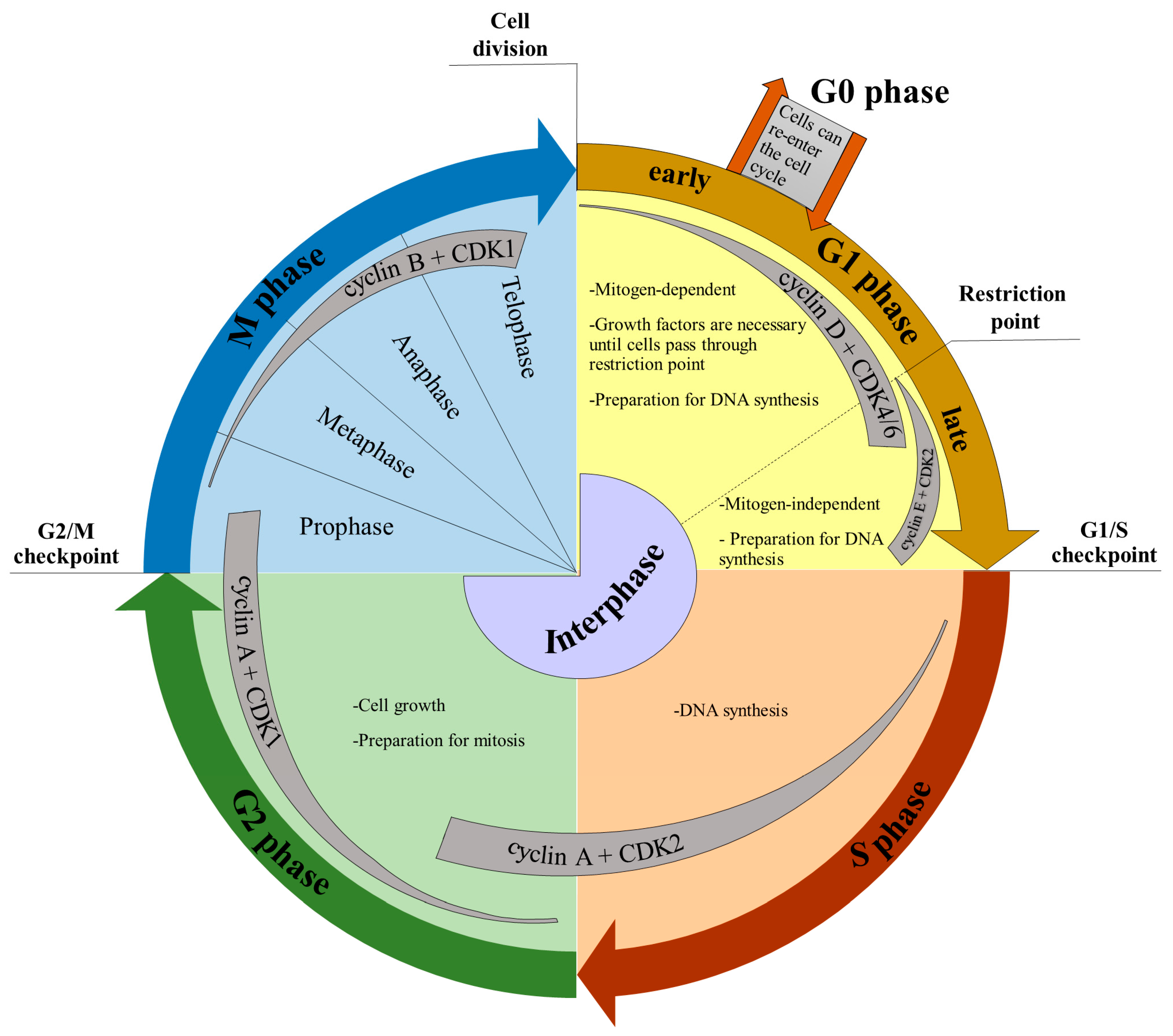
Definition, Phases, Examples, Regulation Biology Diagrams
The cell cycle is the process a cell undertakes to replicate all of its genetic material and divide into two identical cells. In this article, we will look at the different stages of this and what happens in each stage. We will also consider the regulation of the cell cycle, and look at some examples of its dysregulation.
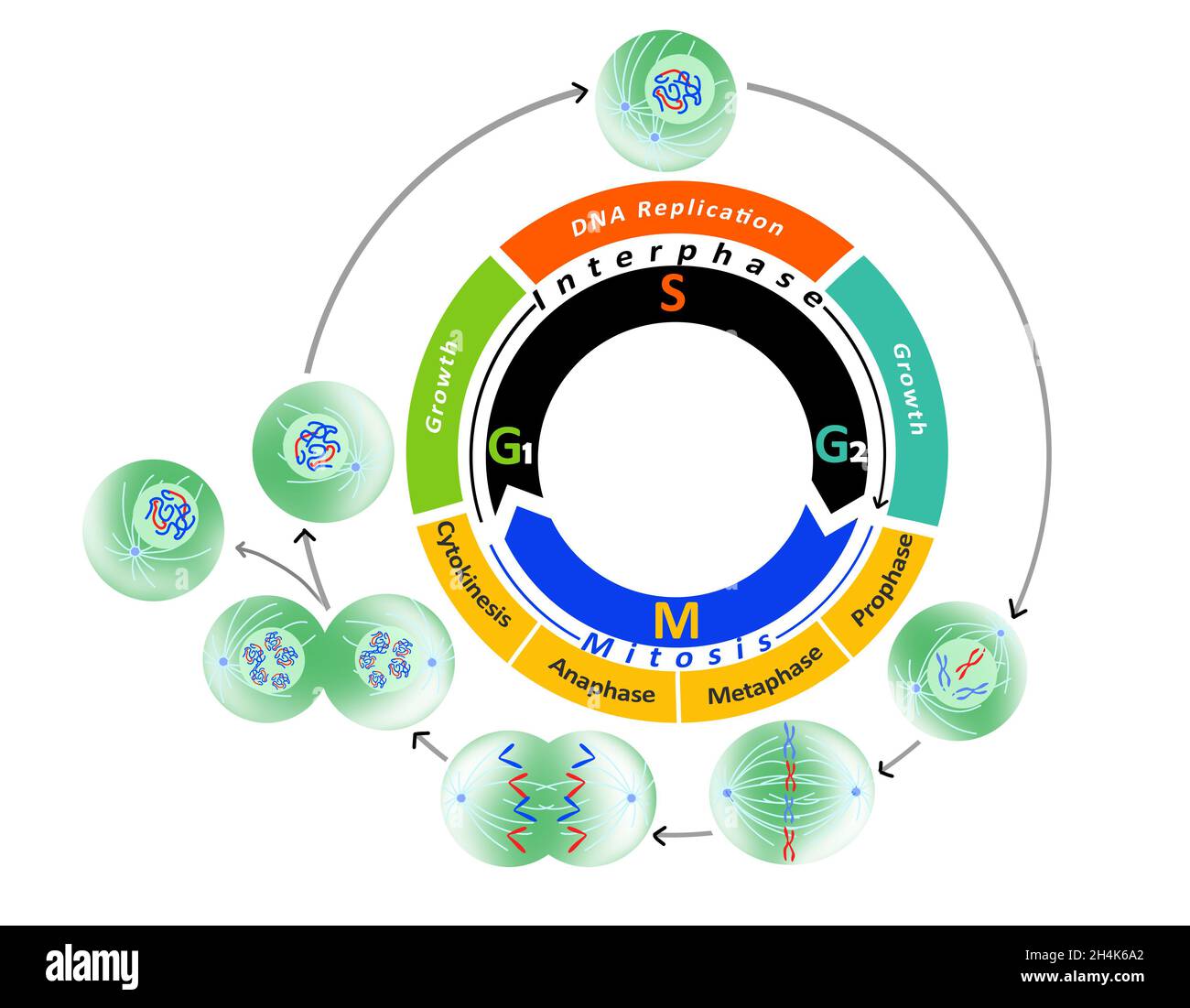
Cell cycle is the name we give the process through which cells replicate and make two new cells. Cell cycle has different stages called G1, S, G2, and M. G1 is the stage where the cell is preparing to divide. To do this, it then moves into the S phase where the cell copies all the DNA. So, S stands for DNA synthesis.

Chromosomes, Genes, and Traits: An Introduction to ... Biology Diagrams
The cell cycle is the sequence of events occurring in an ordered fashion which results in cell growth and cell division. G0, G1, S, G2, M. A cell entering the M phase has a 4N concentration of genetic material and ends with two cells, each containing a 2N concentration of DNA. Mitotic cell division occurs via four distinct steps; Explore the intricate stages of the cell cycle, from growth and DNA replication to chromosome alignment and division, and understand its regulation. In the S phase of the cell cycle, the primary task is the replication of DNA, ensuring that each daughter cell receives an exact copy of the genetic material. This phase is marked by a highly