SOLUTION anatomy anatomy of urinary bladder urethra faculty of medical Biology Diagrams Urinary bladder (sagittal view) The urinary bladder is a pelvic organ that collects and holds urine before urination. It serves as a temporary reservoir for urine produced by the kidneys.When empty, it lies completely within the pelvic cavity, but enlarges upward into the abdominal cavity when full.It is the most anterior pelvic organ, located just behind the pubic bones and pubic symphysis.

The urinary bladder and urethra are pelvic urinary organs whose respective functions are to store and expel urine outside of the body in the act of micturition (urination). As is the case with most of the pelvic viscera, there are differences between male and female anatomy of the urinary bladder and urethra. In our entire urinary system series, the urinary bladder and urethra represent the

Bladder: Anatomy, Location, Function & Related Conditions Biology Diagrams
It is a small tube leading from the urinary bladder to the exterior of the body. In males, the urethra extends through the penis, is about 20 cm in length, and is divided into three regions: the prostatic, membranous and spongy urethra. In males, the urethra also functions to transport semen, formed by the testes and accessory sex glands. The urethra in both males and females begins inferior and central to the two ureteral openings forming the three points of a triangular-shaped area at the base of the bladder called the trigone (Greek tri- = "triangle" and the root of the word "trigonometry").The urethra tracks posterior and inferior to the pubic symphysis (see Figure 4).

The urethra is the vessel responsible for transporting urine from the bladder to an external opening in the perineum.. It is lined by stratified columnar epithelium, which is protected from the corrosive urine by mucus secreting glands.. In this article, we shall look at the anatomy of the male and female urethra - their anatomical course, neurovascular supply, and any clinical correlations.
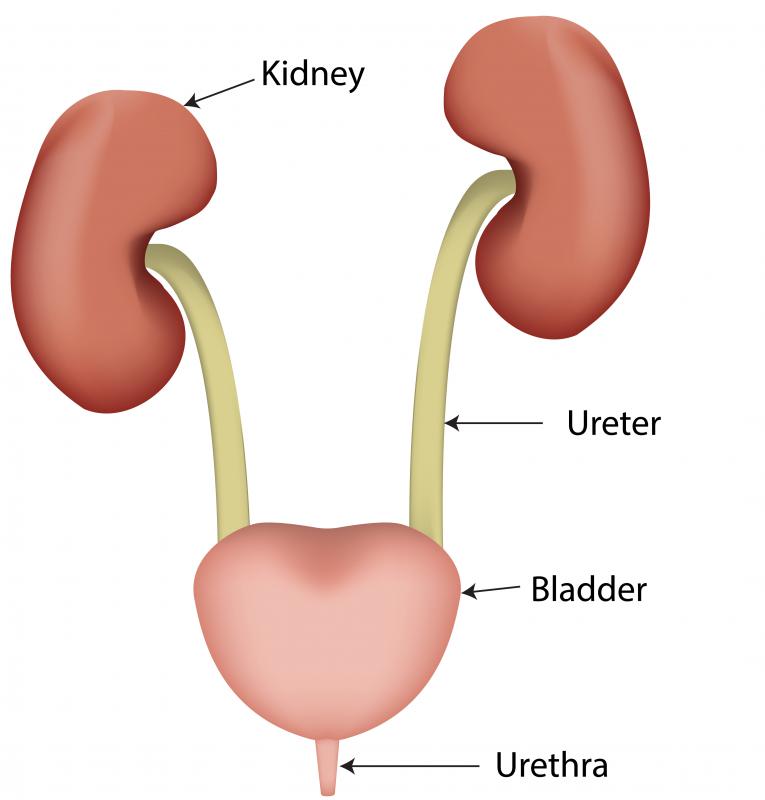
Anatomy of the Urinary System Biology Diagrams
This page discusses the anatomy and function of the urethra, highlighting differences between males and females. The urethra transports urine from the bladder to the outside of the body for disposal. The urethra is the only urologic organ that shows any significant anatomic difference between males and females; all other urine transport The nerves alert a person when it is time to urinate, or empty the bladder. Urethra. This tube allows urine to pass outside the body. The brain signals the bladder muscles to tighten, which squeezes urine out of the bladder. At the same time, the brain signals the sphincter muscles to relax to let urine exit the bladder through the urethra.
