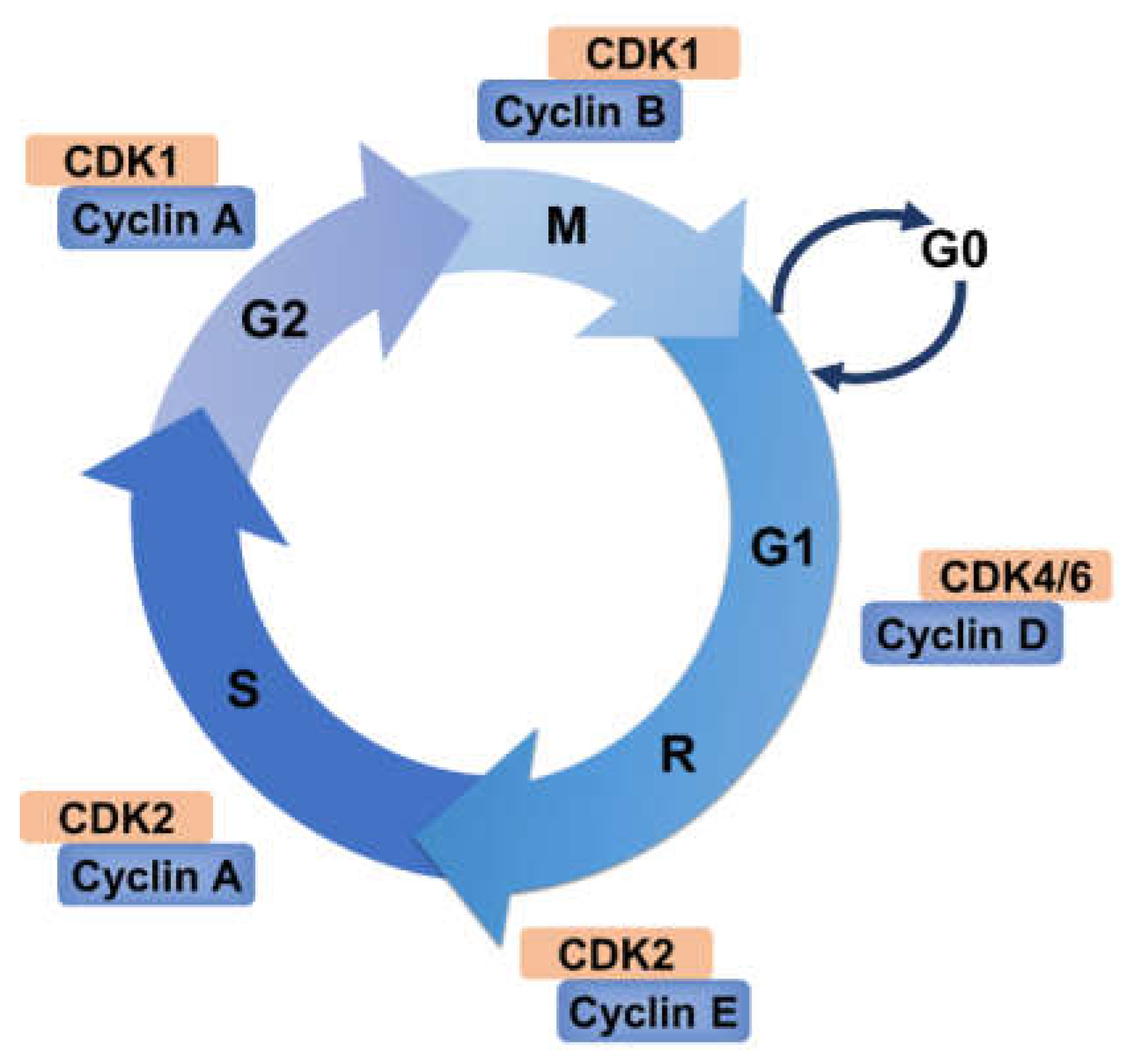
Ubiquitin Ligases Cell Cycle Control And Cancer Biology Diagrams Ubiquitin is an ubiquitously expressed small regulatory protein in living cells [].The addition of ubiquitin to a substrate protein is called ubiquitination, which is catalyzed by three types of Dang et al. discuss how ubiquitination, particularly the two E3 ubiquitin ligases anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C) and the Skp1-Cul1-F-box 8 (SCF) complex, regulate cell cycle Besides tagging proteins for degradation, ubiquitin is now recognized as a signaling module for diverse cellular processes, including progression through the cell cycle, DNA repair, gene transcription, receptor trafficking and endocytosis. Recent advances have indicated the existence of a wide varie …

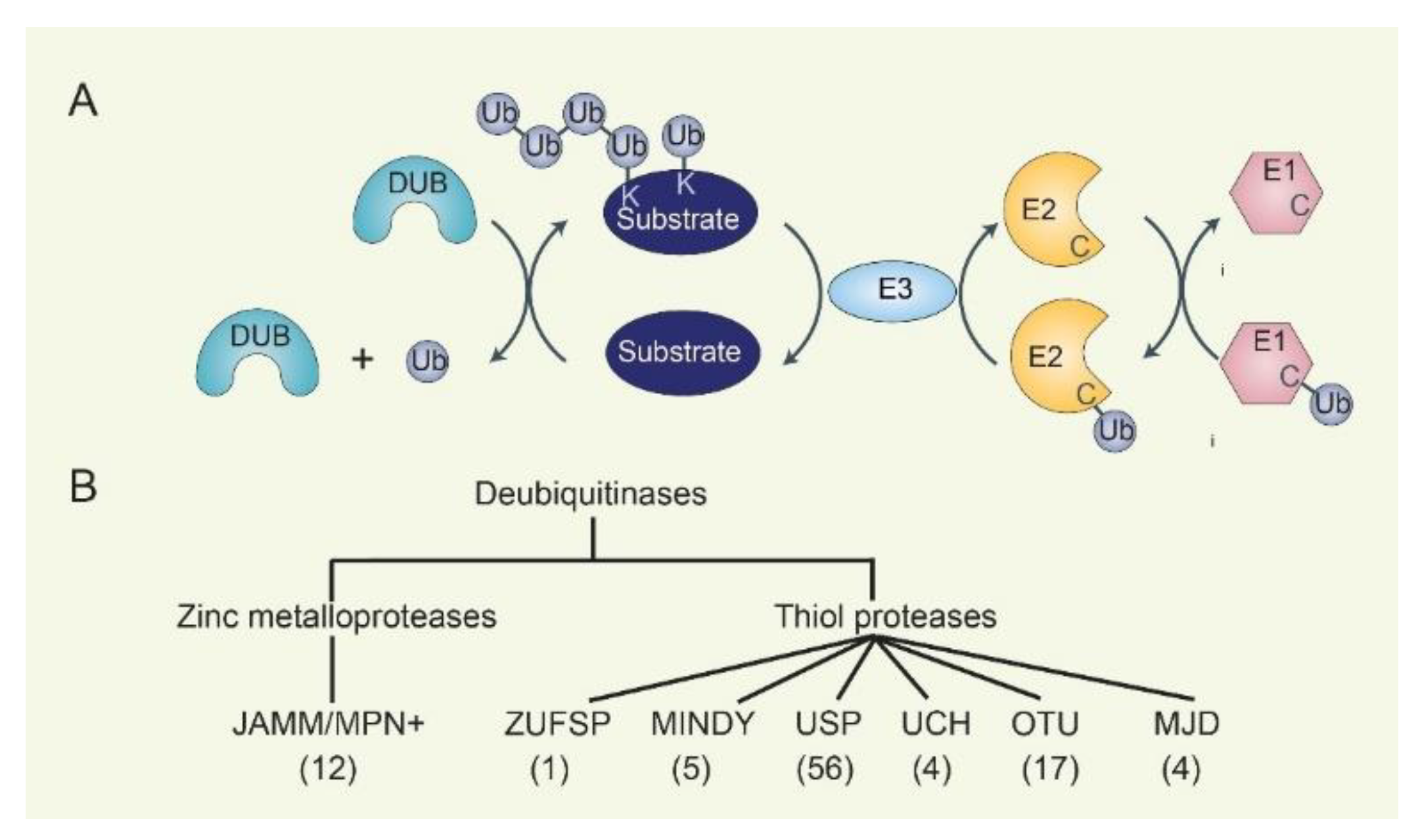
Contrary to reversible modifications, such as phosphorylation or association with CKIs, ubiquitin-mediated proteasomal degradation is an irreversible mechanism that assures the strict unidirectionality of the cell cycle, and it plays a key role in cell cycle regulation by mediating the precise spatial and temporal proteolysis of the main The SAC generates a diffusible "wait anaphase" signal through unattached kinetochores. 162 In securin‐deficient cells, researchers have identified human shugoshin 2 (Sgo2), which forms a complex with mitotic‐arrest deficient‐1 (Mad2), substituting the role of securin in these cells. 163 The interplay between APC/C, the SAC, and early Several ubiquitin ligases are altered in cancer. These proteins are crucial for the ubiquitin-mediated degradation of cell-cycle proteins, ensuring regulated progression through the cycle.
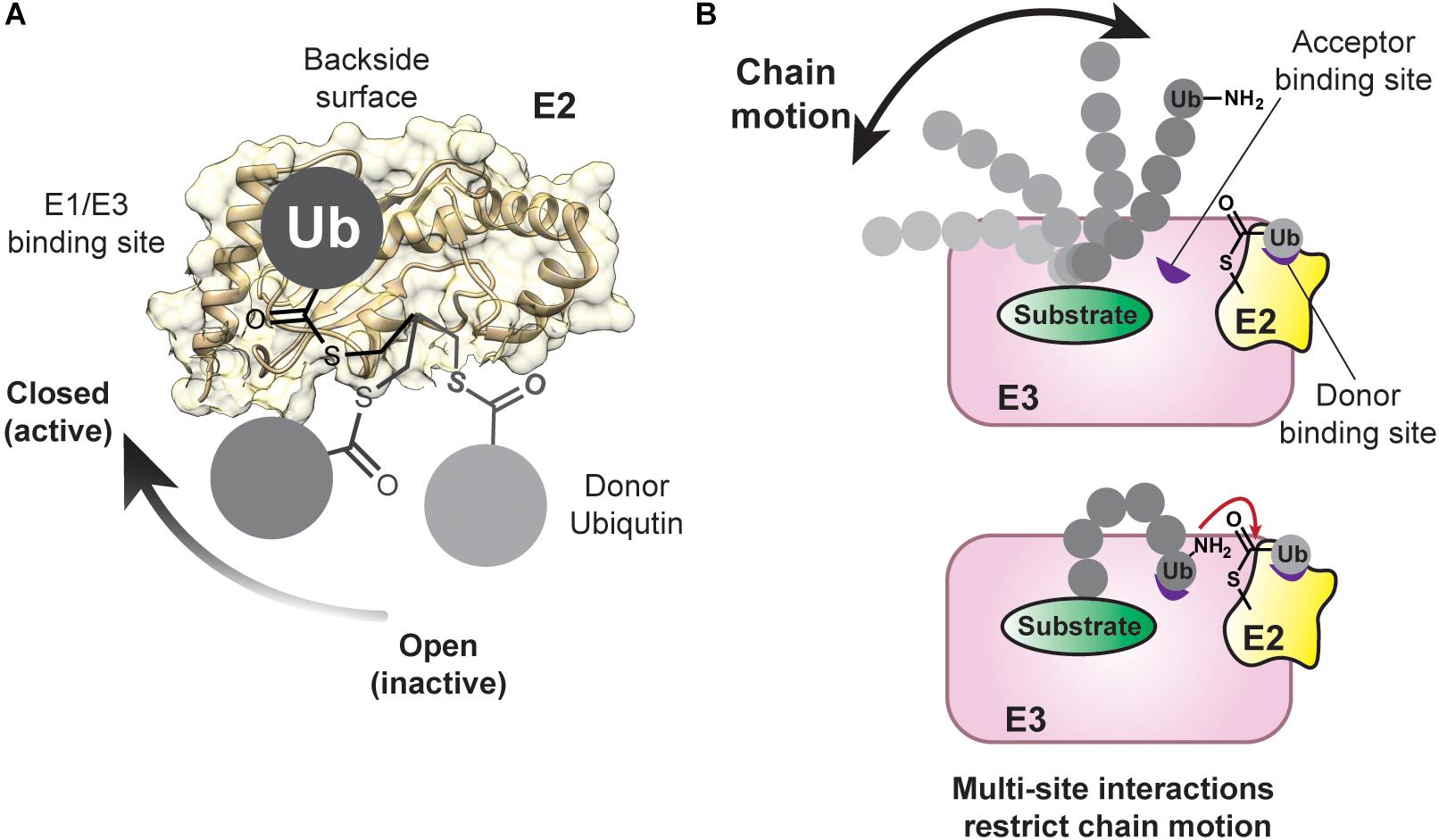
binding proteins in cell signaling Biology Diagrams
The small protein ubiquitin plays a vital role in virtually all aspects of cellular life. Among the diverse signaling outcomes associated with ubiquitination, the most well-established is the targeted degradation of substrates via the proteasome. During cell growth and proliferation, ubiquitin plays an outsized role in promoting progression through the cell cycle.
The anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C) exemplifies this strategy, as it employs substrate adaptors such as Cdh1 and Cdc20 to mediate cell cycle-dependent ubiquitination. This modular approach enhances specificity and allows for temporal regulation, ensuring proteins are ubiquitinated only at appropriate stages of the cell cycle. In the cell cycle, ubiquitination plays a central role in cell cycle transitions and checkpoints by establishing the strict temporal control of proteins such as cyclins, CDKs, CKIs, other kinases and phosphatases . The UPS is one of the protein degradation pathways in eukaryotic cells, and most proteins rely on this system for degradation.